In today’s interconnected world, where the flow of information can shape perceptions and influence decisions in the blink of an eye, the importance of due diligence has never been more critical. Enter the realm of Adverse Media Screening, a pivotal yet often overlooked component of risk management that seeks to unveil hidden narratives surrounding individuals, organizations, and entities. This meticulous process goes beyond traditional background checks, tapping into a vast array of news stories, social media accounts, and other publicly available data to identify potential red flags that may not be immediately obvious. As businesses, financial institutions, and even individuals navigate the complex landscape of reputational risk, understanding and implementing effective adverse media screening strategies has become essential. Join us as we explore the intricacies of this vital practice, its implications for risk assessment, and its role in safeguarding integrity in an increasingly transparent world.
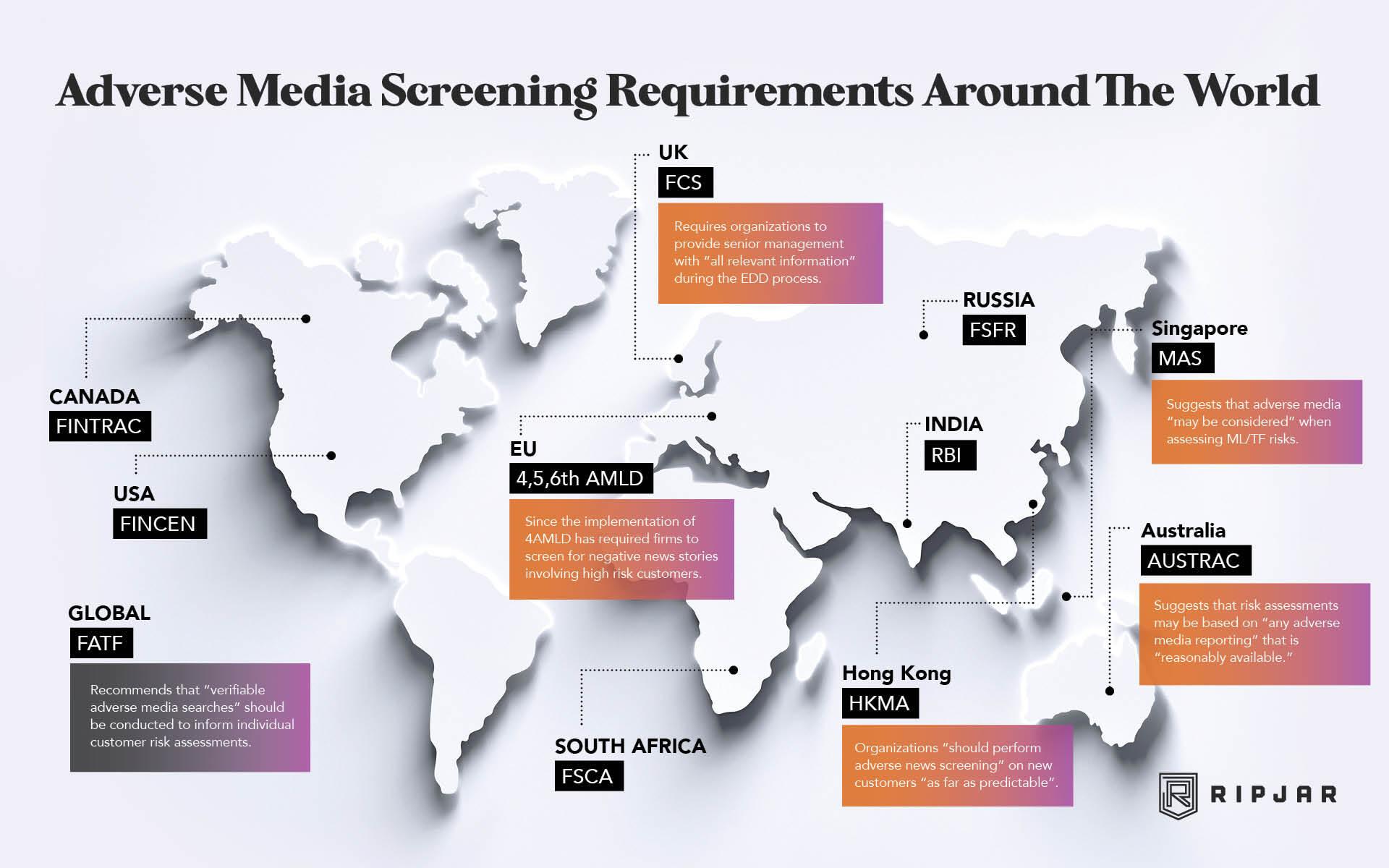
Understanding Adverse Media Screening and Its Importance in Risk Management
Adverse media screening plays a vital role in modern risk management by identifying potential threats to an organization’s integrity and reputation. By systematically examining news, social media, and other public platforms, businesses can uncover information that might affect their operational environment. The process enables organizations to assess potential risks related to stakeholders, including clients, partners, and employees, through a range of methods such as:
- Comprehensive database searches to find relevant articles and reports.
- Real-time monitoring of various media outlets to stay updated on emerging risks.
- Contextual analysis to understand the implications of reported information.
Effective adverse media screening not only enhances due diligence practices but also aids in compliance with regulatory requirements. By integrating this screening into the overall risk management strategy, companies can mitigate potential fallout from negative associations. The following table illustrates key components of an effective adverse media screening process:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Sources | News articles, blogs, and social media platforms |
| Frequency | Real-time or periodic checks |
| Analysis Tools | Natural Language Processing and AI algorithms |
| Reporting | Detailed summaries highlighting risks and insights |
Key Techniques for Effective Adverse Media Screening Implementation
Implementing an effective adverse media screening system requires a deep understanding of both technology and industry nuances. Leveraging advanced algorithms allows organizations to sift through vast amounts of data efficiently, identifying relevant mentions of individuals or entities in connection with adverse events. Machine learning models can be trained to refine the screening process over time, adapting to new types of media sources and shifting risk factors. It’s essential to ensure these algorithms are regularly updated and monitored to capture significant changes in the media landscape, thereby minimizing false positives and negatives.
Moreover, establishing a culture of compliance and awareness within the organization can greatly enhance adverse media screening efforts. Regular training sessions for employees should be conducted to familiarize them with the importance of vigilance in monitoring potential risks. Integrating collaborative tools can encourage teams to share insights and findings related to adverse media, fostering a proactive approach to risk management. Additionally, implementing a structured feedback loop between screens and investigations ensures continuous improvement in the screening process.

Navigating Privacy Concerns in Adverse Media Investigations
Adverse media investigations often collide with privacy regulations, urging organizations to find a balance between comprehensive risk assessments and respecting individual privacy rights. When scrutinizing adverse media, it is vital to consider the scope of the investigation and ensure compliance with data protection laws like the GDPR or CCPA. This involves understanding what constitutes permissible data and ensuring that the information collected is both relevant and necessary for the investigation. The challenge lies in mitigating reputational risk while maintaining ethical standards; thus, a clear framework for this process is essential.
Additionally, organizations should implement robust policies to handle sensitive data judiciously. Establishing a protocol for data retention and access controls can help safeguard individual privacy and confidential information. Key practices include:
- Minimization of Data Collected: Only gather data that is essential for the assessment.
- Transparency: Clearly communicate to stakeholders how their data will be used.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic checks to ensure compliance with regulations and internal policies.
By embedding these strategies into the adverse media screening process, organizations can effectively navigate the complexities of privacy concerns, fostering a culture of responsible and ethical data usage.
Best Practices for Interpreting Results and Making Informed Decisions
When interpreting results from adverse media screening, it is crucial to approach the findings with a balanced perspective. Contextualizing the data is essential; it’s important to assess the nature and credibility of the sources referenced in the screening reports. Look for patterns in the data that may indicate a significant issue versus isolated incidents. Consider engaging with subject matter experts or industry peers to verify insights and gain alternative viewpoints. Cultivating a critical approach not only helps to mitigate risks but also fosters a comprehensive understanding of your subject.
Beyond interpretation, there should be a structured approach to decision-making based on these insights. Here are some recommended actions to take:
- Prioritize Findings: Distinguish between high, medium, and low-risk findings to allocate resources effectively.
- Define Clear Objectives: Outline what you aim to achieve through informed decisions and align them with organizational goals.
- Implement Feedback Loops: Create channels for continuous feedback to refine processes and improve future screening efficacy.
Consider using a decision matrix to visualize options and outcomes, ensuring you are equipped to choose the best course of action:
| Option | Risks Involved | Benefits | Priority Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increase Monitoring | Medium | Enhanced awareness of risks | High |
| Engage Experts | Low | Informed decision-making | Medium |
| Ignore Flags | High | Short-term ease | Low |
Closing Remarks
In a world where information flows ceaselessly and every action can be scrutinized through a digital lens, the importance of Adverse Media Screening is undeniable. As businesses and individuals grapple with the complexities of reputation management and compliance, the practice serves as a crucial shield against potential pitfalls. By leveraging advanced technologies and analytical frameworks, organizations can not only safeguard their interests but also foster transparency and trust in their interactions. In this ever-evolving landscape, remaining vigilant and informed is paramount, and Adverse Media Screening stands as a formidable ally. As we navigate the intricate web of information, the ability to discern risk from opportunity will continue to shape how we approach our endeavors in an interconnected world. Ultimately, the key to a resilient future lies in our capacity to embrace these insights, turning vigilance into an asset rather than a burden.


